Update Ruby For Mac
With package managers or third-party tools, you have plenty of optionsto install and manage Ruby.
I have created a new user account on my mac and I am trying to update to the current version of ruby on it (1.9.2) from the snow leopard default of 1.8.7. Can somebody point me to tutorial or explain the best method to update Ruby on my mac from 1.8 to 1.9.2? How to Install Ruby on Mac OS X with RVM. This article explains why you should avoid using the version of Ruby bundled with Mac OS X and should instead install your own version of Ruby with RVM, the Ruby Version Manager. Hands Off the System Ruby. Apple bundles the Ruby programming language with OS X. However, the main caveat for using the.
You may already have Ruby installed on your computer. You can checkinside a terminal emulator by typing:
This should output some information on the installed Ruby version.
Choose Your Installation Method
There are several ways to install Ruby:
- On a UNIX-like operating system, using your system’spackage manager is easiest.However, the packaged Ruby version may not be the newest one.
- Installers can be used to install a specific or multipleRuby versions. There is also an installer for Windows.
- Managers help you to switch between multiple Ruby versionson your system.
- Finally, you can also build Ruby from source.
On Windows 10, you can also use the Windows Subsystem for Linuxto install one of the supported Linux distributions and use any of theinstallation methods available on that system.
Here are available installation methods:
- Package Management Systems
- Installers
- RubyInstaller (Windows)
- Managers
Package Management Systems
If you cannot compile your own Ruby, and you do not want to use athird-party tool, you can use your system’s package manager to install Ruby.
Some members of the Ruby community feel that you should avoid packagemanagers to install Ruby and that you should use dedicated tools instead.
It is possible that major package managers will install older Rubyversions instead of the latest release. To use the latest Ruby release,check that the package name matches its version number. Or use adedicated installer.
apt (Debian or Ubuntu)
Debian GNU/Linux and Ubuntu use the apt package manager. You can use itlike this:
yum (CentOS, Fedora, or RHEL)
CentOS, Fedora, and RHEL use the yum package manager.You can use it like this:
The installed version is typically the latest version of Ruby availableat the release time of the specific distribution version.
snap (Ubuntu or other Linux distributions)
Snap is a package manager developed by Canonical.It is available out-of-the-box on Ubuntu, but snap also workson many other Linux distributions.You can use it like this:
We have several channels per Ruby minor series.For instance, the following commands switch to Ruby 2.3:
portage (Gentoo)
Gentoo uses the portage package manager.
To install a specific version, set RUBY_TARGETS in your make.conf.See the Gentoo Ruby Project website for details.
pacman (Arch Linux)
Arch Linux uses a package manager named pacman.To get Ruby, just do this:
This should install the latest stable Ruby version.
Homebrew (macOS)
Ruby versions 2.0 and above are included by default in macOS releasessince at least El Capitan (10.11).
Homebrew is a commonly used package manager on macOS.Installing Ruby using Homebrew is easy:
This should install the latest Ruby version.
FreeBSD
FreeBSD offers both pre-packaged and source-based methods to install Ruby.Prebuilt packages can be installed via the pkg tool:
A source-based method can be used to install Ruby using thePorts Collection. This is useful if you wantto customize the build configuration options.
More information about Ruby and its surrounding ecosystem on FreeBSDcan be found on the FreeBSD Ruby Project website.
Ruby on OpenIndiana
To install Ruby on OpenIndiana, please use theImage Packaging System (IPS) client.This will install the Ruby binaries and RubyGems directlyfrom the OpenIndiana repositories. It’s easy:
However, the third-party tools might be a good way to obtain thelatest version of Ruby.
Other Distributions
On other systems, you can search the package repository of your Linuxdistribution’s manager for Ruby. Alternatively, you can use athird-party installer.
Installers
If the version of Ruby provided by your system or package manager is outof date, a newer one can be installed using a third-party installer.
Some installers allow you to install multiple versions on the samesystem; associated managers can help to switch between the differentRubies.
If you are planning to use RVM as a version manager you don’tneed a separate installer, it comes with its own.
ruby-build
ruby-build is a plugin for rbenv that allows youto compile and install different versions of Ruby. ruby-build can alsobe used as a standalone program without rbenv. It is available for macOS,Linux, and other UNIX-like operating systems.
ruby-install
ruby-install allows you to compile and install differentversions of Ruby into arbitrary directories. chruby is acomplimentary tool used to switch between Ruby versions. It is availablefor macOS, Linux, and other UNIX-like operating systems.
RubyInstaller
On Windows, RubyInstaller gives you everything you needto set up a full Ruby development environment.
Just download it, run it, and you are done!
Ruby Stack
If you are installing Ruby in order to use Ruby on Rails,you can use the following installer:
- Bitnami Ruby Stack provides a complete developmentenvironment for Rails. It supports macOS, Linux, Windows, virtualmachines, and cloud images.
Managers
Many Rubyists use Ruby managers to manage multiple Rubies. They alloweasy or even automatic switching between Ruby versions depending on theproject and other advantages but are not officially supported. You canhowever find support within their respective communities.
asdf-vm
asdf-vm is an extendable version manager that can manage multiplelanguage runtime versions on a per-project basis. You will need theasdf-ruby plugin (which in turn uses ruby-build)to install Ruby.
chruby
chruby allows you to switch between multiple Rubies. It canmanage Rubies installed by ruby-install or even builtfrom source.
rbenv
rbenv allows you to manage multiple installations of Ruby.While it can’t install Ruby by default, its ruby-buildplugin can. Both tools are available for macOS, Linux, or otherUNIX-like operating systems.
RVM (“Ruby Version Manager”)
RVM allows you to install and manage multiple installations ofRuby on your system. It can also manage different gemsets. It isavailable for macOS, Linux, or other UNIX-like operating systems.
uru
Uru is a lightweight, multi-platform command line tool that helps youto use multiple Rubies on macOS, Linux, or Windows systems.
Building from Source
Of course, you can install Ruby from source.Download and unpack a tarball, then just do this:
By default, this will install Ruby into /usr/local.To change, pass the --prefix=DIR option to the ./configure script.
You can find more information about building from source in theRuby README file.
Using the third-party tools or package managers might be a better idea,though, because the installed Ruby won’t be managed by any tools.
Install Command Line Tools
To install the command line tools to compile native extensions, open a terminal and run:
Install Ruby
Jekyll requires Ruby v2.5.0 or higher.macOS Catalina 10.15 ships with Ruby 2.6.3. Check your Ruby version using ruby -v.
If you’re running a previous version of macOS, you’ll have to install a newer version of Ruby.
With Homebrew
To run the latest Ruby version you need to install it through Homebrew.
Add the brew ruby path to your shell configuration:
Relaunch your terminal and check your Ruby setup:
You’re now running the current stable version of Ruby!
With rbenv
People often use rbenv to manage multipleRuby versions. This is very useful when you need to be able to run a given Ruby version on a project.
Restart your terminal to apply your changes.Next, you can install the Ruby version you want. Let’s install the latest stable version:
That’s it! Head over to rbenv command references to learn how to use different versions of Ruby in your projects.
Install Jekyll
After installing Ruby, install Jekyll and Bundler.
Local Install
Install the bundler and jekyll gems:

Get your Ruby version:
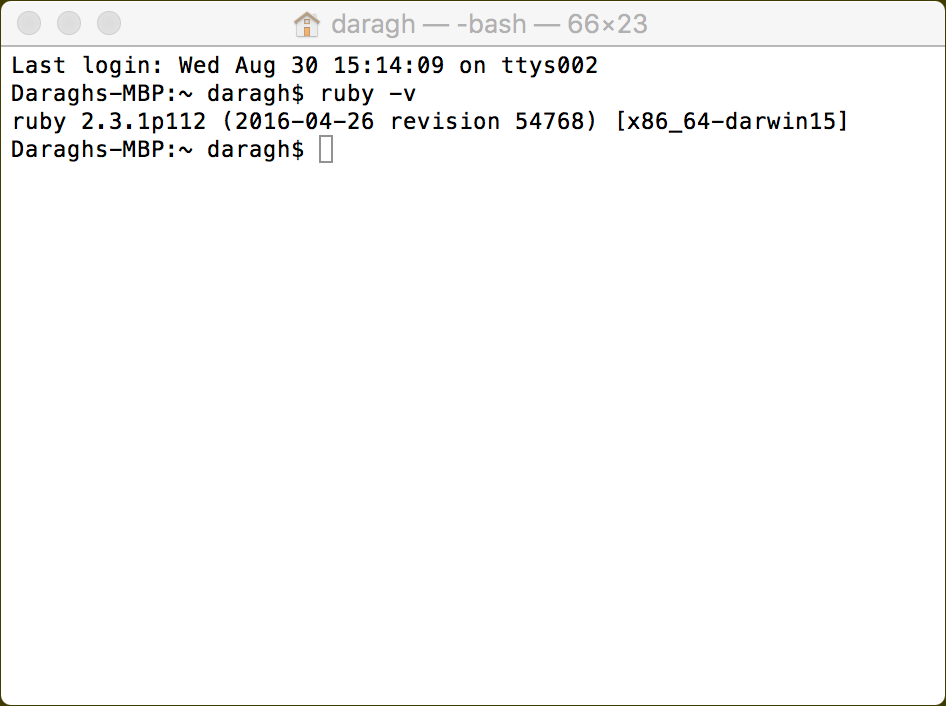
Append your path file with the following, replacing the X.X with the first two digits of your Ruby version:
Check that GEM PATHS: points to your home directory:
Every time you update Ruby to a version in which the first two digits change, update your path to match.
Global Install
We recommend not installing Ruby gems globally to avoid file permissions problems and using sudo.
On Mojave (10.14)
Update Ruby For Mac High Sierra
Because of SIP Protections in Mojave, run:
Before Mojave (<10.14)
Update Ruby Mac Mojave
Run:
Troubleshooting
Update Ruby Terminal
See Troubleshooting or ask for help on our forum.